Article by CDA
News, information and news are always around us, influencing our lives, sometimes for better or worse. Some of them are false, doing us a disservice, both personally and to society as a whole.
In the context in which the information circulated in the public space directly affects us and helps us to make various decisions, it is important to learn how to develop critical thinking and to recognize and combat the phenomenon of “fake news”. Lately we hear around us that various public institutions, media, social networks are fighting against this phenomenon. So we end up asking ourselves a few questions: How dangerous is the phenomenon of false news? How does it affect us? How do we filter the information that bombards us daily?
Social networks are the channels that spread misinformation, – including “fake news”. The right approach to combating misinformation that media companies such as Facebook and Twitter currently use is to use fact-checkers to identify and label false or misleading statements.
By verifying the truth of the facts, the proliferation and impact of misinformation can be considerably reduced. Social media platforms can use fact checking to influence the likelihood that certain pieces of content will be displayed to users. In-depth verification is a fairly extensive process, and you often can’t keep up with the sheer amount of content posted on social media every day. In addition, even when fact-finding warnings are successfully applied to misinformation, their impact may be reduced due to a lack of trust. For example, according to a Poynter study, 70% of Republicans and 50% of Americans generally believe that fact-checkers are biased and do not trust fact-finding corrections.
Some practical fact checking tools
Search for images in reverse mode – The Google Images algorithm is able to find similar or visually identical images on the web
Intuition is far more important than online search algorithms
Pay attention to the inclination towards confirmation! – We are not just about titles! We also read the content!
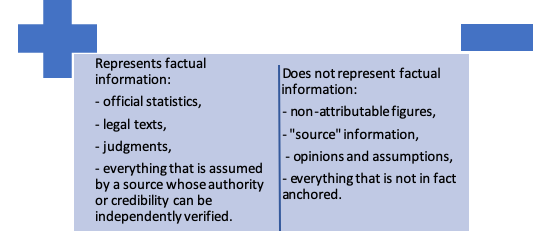
Learn what factual information is
Aesthetic criteria – The title begs the click (“clickbait”) is enticing (“You won’t believe it ….…”, “SHOCKING!” Or “Incredible,…”), or the article itself is messy, alarmist, with capital letters and bold. Check the date – Some sources publish old news, irrelevant to current events.
How we treat information to become misinformation?
DENIAL OF FACTS (It’s not true that …)
REVERSE OF FACTS ( This is not what happened, but on the contrary …)
THE MIXTURE BETWEEN TRUTH AND LIE ( It’s true that … but that’s because …)
MODIFICATION OF THE REASON (The reason … is not the same, but the fact that …)
BLURRING (There is too much noise on this subject; others do much worse and nothing happens!)
GENERALIZATION (Everyone does this …; how did you find him / her guilty?)
USE OF UNEQUAL PARTS( In the case of publicizing the event, a limited space will be given to the fact itself, and highlighting the moral qualities and good deeds of the subject will occupy a much larger space).

